Insights
Innovation in Product Warranty Management - Part One
2023-11-13 09:42:45
Innovation in Product Warranty Management
Under the guidance of Industry 4.0 and intelligent technology, the era of emerging technology trends has arrived. Whether it is robot technology or artificial intelligence, automation, advanced materials and manufacturing, the Internet of Things, cloud computing, big data, augmented reality, network security, and data processing, innovation in warranty management has found direction. Even recent popular ChatGPT can improve customer service quality. Or through measurement of product operating parameters, data statistics and judgment can be made, early-warning system can be issued to assist in design corrections and maintenance solutions. The idea of tracking the entire product lifecycle is no longer out of reach. From sales behavior to customer usage status, to after-sales warranty process management, and even to final recycling and scrapping.
Digital Technology | |
The development of technology has brought huge changes to life. Often before adapting to the changes brought by new technologies, the next generation of technology has quietly arrived. Whether it is digital and network technology, the Internet of Things and human body function, innovation and industrial competitiveness, medical and synthetic biology, and environment and sustainability, all face different levels of challenges [1]. The Internet of Things is a new perspective that provides recommendations for optimizing factory and service operations through monitoring IoT node networks. It is estimated that there will be over 17.2 billion connected devices by 2023, as shown in Figure 1. Whether product failure or recall is due to independent events or component failures, data analysis through the IoT can easily perform large-scale warranty service analysis or assign nearby technicians to solve damaged/worn parts, effectively improving product availability and safety. |
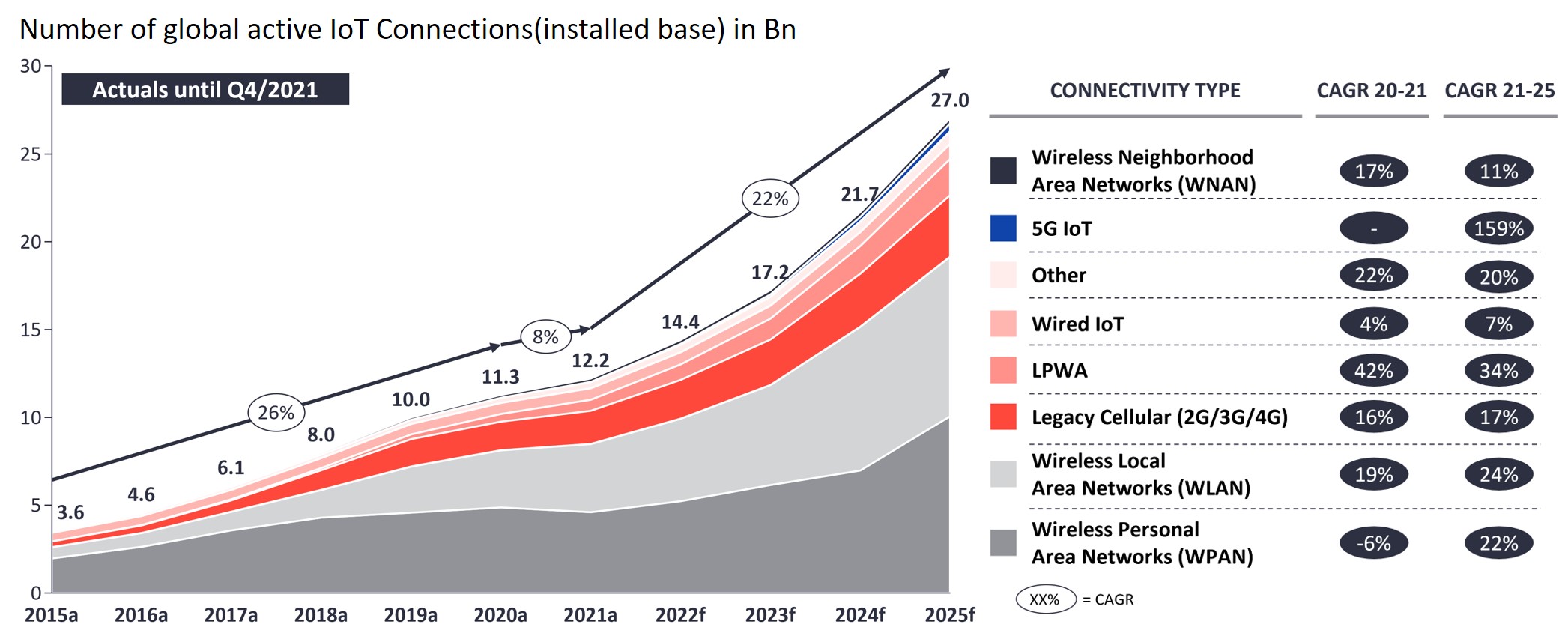
Figure 1. Growth trend of IoT devices. [2]
In response to the development of Industry 4.0, after-sales warranty is also undergoing transformation. By relying on the architecture of industrial Internet and the Internet of Things, and based on cloud computing and platforms, a service-centered warranty system is established to strengthen products in after-sales warranty, even throughout the entire product life cycle management, until scrapping and recycling establish an ESG system. In the digital transformation of the industry, as products become more complex, it is an urgent problem for enterprises to establish effective after-sales service and warranty management while taking business operations and costs control into account. | |
Warranty Costs | |
EEnterprises will set target costs for after-sales warranty in product design and sales. Through reasonable warranty management, they can effectively control costs and keep expenses lower than the original set target. Even profits can be gained from non-warranty services. In the low profitability competition of mature industries, how to manage warranty costs is crucial. After the manufacturer sells the product, they should provide a certain degree of warranty service. Although the current business model has shifted to product services, most products still come with warranty services to ensure product quality. As long as there is a warranty requirement, the manufacturer will incur additional costs, known as warranty costs. There is a lot of uncertainty in analyzing warranty costs. The quality of each product will differ due to design, production assembly errors, or supplier parts quality, and the customer's usage environment is also a variable. | |
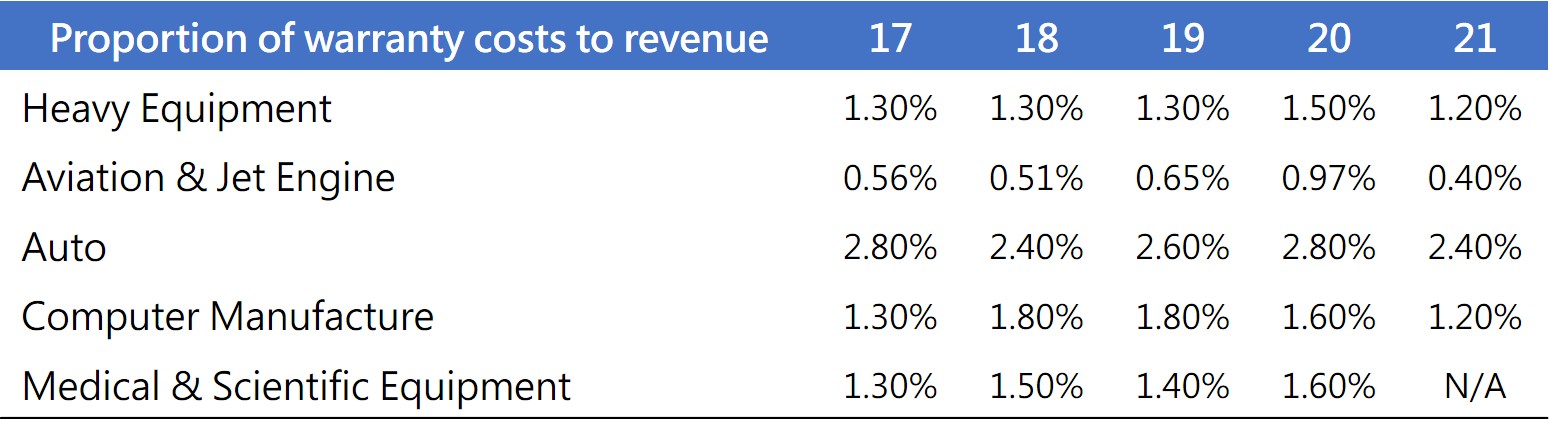
For many enterprises, warranty costs are roughly equivalent to R&D costs. While it is important to focus on the core value of enterprise R&D, it is impossible to ignore warranty costs. Effective warranty cost management is not only about cost control, but also serves as a management indicator for product warranty policies and product quality. Overall, warranty costs can be divided into five categories: warranty service, material costs, return logistics, cost management, and quality assurance. The proportions of each cost category will vary across industries due to differences in warranty types, as shown in Table 1. | |
Table1. Warranty Management Cost Proportion of Major Industries in the United States [3] |
Reference to International Accounting Standard (IAS 37) and International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS 15) requirements for warranty costs, warranty costs can be estimated annually based on the number of product sales, expected failure rate, and the product of the average warranty costs for each failure [4]. In addition to estimating the number of warranties through product reliability, another key is to handle abnormalities, repair defective products, replacement, or service average costs. To effectively reduce these costs and the probability of product returns, in addition to improving product reliability, reducing the average maintenance costs can also reduce the overall warranty costs. | |
Management Innovation | |
The purpose of establishing warranty management capabilities in enterprises is not only to effectively manage after-sales service to improve customer satisfaction, but also to focus on controlling warranty costs. These should not only provide customers with complaint channels, but also establish corresponding management processes, including data analysis, reliability estimation, warranty policy management, etc. The accuracy of data analysis and the selection of reliability models will affect the accuracy of costs analysis. Therefore, it must be continuously revised based on actual warranty data. The calculated warranty costs after data cleaning can be used as a basis for improving efficiency or products, and even displaying early warning. The basic logic of costs analysis is understood through the two main variables of warranty policy and warranty quantity. The costs model mainly starts from the perspective of the manufacturer. The warranty analysis model and the warranty conditions it provides are related to the distribution of defective products. The costs will change over time, and exchange rates, labor, etc. may cause errors in costs analysis. This is a very complex problem, even product marketing and regulations must be considered. [5] | |
Good product design and high reliability of products can reduce repair rates and warranty costs, but how to balance the product design costs and timeliness, as well as warranty service operations, customer satisfaction and warranty costs, and integrate these important considerations in warranty management, not only need to consider warranty policies, warranty services, product reliability, and relationships with competitors externally, but also track product warranty services internally, and repair or service in a timely manner to reduce customer complaints, while ensuring warranty management operation processes and costs. All of these should be considered in the previous product marketing strategy and pricing conference. When enterprises focus on their core competencies, if they neglect the importance of warranty management in the scheduling of product development and manufacturing, or even do not have relevant policies and management processes, it may seriously affects the enterprise's profitability. | |
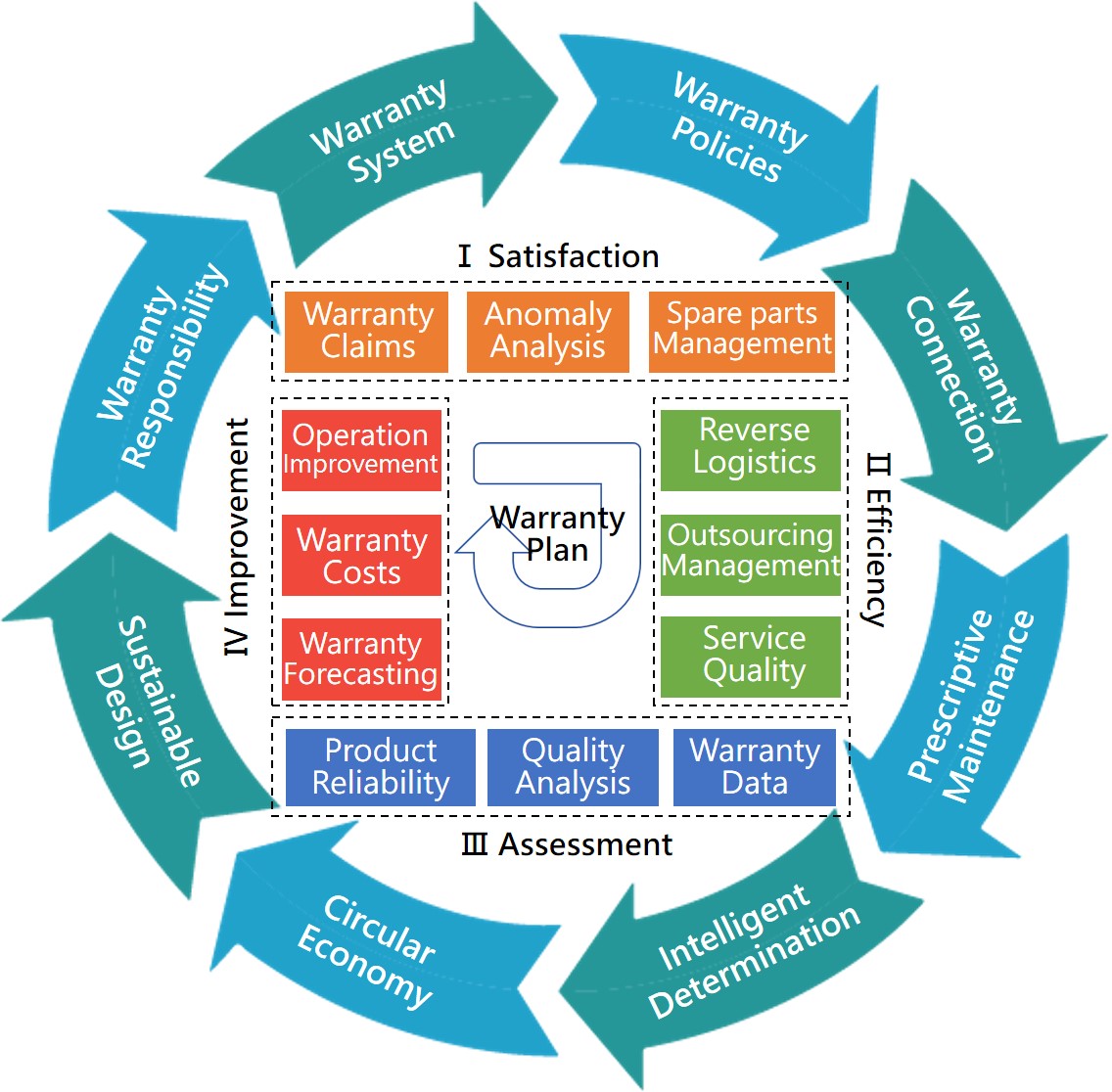
In response to the operation of enterprise management organizations and industry development trends, different from the past, which warranty management mostly focused on a single enterprise. In fact, it also includes related enterprises and industries, outsourcing service providers, and even requires coordination with suppliers to complete warranty services. Unlike reverse logistics that focuses on recycling process control in the past, a Warranty Chain Management system must be constructed to perfect the management of the entire process from product sales and service to recycling and scrapping. Overall warranty management innovation can be divided into two main levels, as shown in Figure 2: |
| |
Figure 2. Elements of warranty chain management [6] |
Author
Dr. Albert Liao
Founder and CEO of Wareconn Technology Services (wareconn.com),
Author of “Warranty Chain Management - Digitalization and Sustainability”, Springer
Reference
- J Augustyn, (2016), Emerging Science and Technology Trends: 2016-2045 – A Synthesis of Leading Forecasts Report”, Office of the Deputy Assistant Secretary of the Army (Research & Technology)
- Mohammad Hasan, 2022, State of IoT 2022: Number of connected IoT devices growing 18% to 14.4 billion globally, IoT Analytics
- Eric Arnum, (2021),Worldwide Auto/HVAC/ Warranty Expenses, warranty week.com.
- IFRS , (2014), IFRS 15: Revenue from Contracts with Customers, Deloitte
- Wallace R. Blischke, M. Rezaul Karim, D. N. Prabhakar Murthy, (2011), Warranty Data Collection and Analysis, Springer London.
- Albert Liao, (2022),Warranty Chain Management - Digitalization and Sustainability, Springer
- Jay lee, Jun Ni, Jaskaran Singh, Baoyang Jiang, Moslem Azamfar, Jianshe Feng, (2020), Intelligent Maintenance Systems and Predictive Manufacturing, Journal of Maufacturing Science and Engineering, Nov.Vol.142, 1100805-1.